Stem Cells
Stem cells are key players in the development, growth and regeneration of living organisms. They are the basis of life, participating in the construction and repair of every tissue and organ in the human body. Their unique ability to differentiate into different cell types makes them a major area of research and application in medical science and biology.
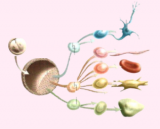
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells, meaning that they are not yet specialised for a specific function in the body. They reside in various tissues, where they wait to receive environmental signals to differentiate into specialised cells, such as heart, nerve, blood and bone cells, and many others.
The fundamental role of stem cells in development begins at conception. When the fertilised egg cell divides and multiplies, some of the resulting cells remain stem cells, while others begin to differentiate into different cell types. This hierarchy of differentiation is what enables the harmonious construction of a complex organism from a single cell.
Beyond embryonic development, stem cells continue to act as an internal maintenance system. They are responsible for regenerating damaged tissue, playing a vital role in healing wounds and repairing worn tissue. Their permanent presence enables the body to maintain its integrity and optimal functioning throughout life.
Stem cells fall into several categories, each with its own specific characteristics. Embryonic stem cells are the most primitive cells and have the potential to differentiate into any cell type. Adult stem cells reside in various tissues and are involved in the regeneration of these specific tissues. Induced stem cells (iPS) are a relatively recent innovation, created by reprogramming adult cells to regain properties similar to those of embryonic stem cells.
By exploring the various types of stem cells, we can better understand their complex role in development, regeneration and potential medical treatments. This exploration opens up promising prospects for regenerative medicine and the fundamental understanding of cell biology.